BCA-2005T (For theory)
BCA-2005P (For practical)
SEC-III – Web Technologies
1L+T: 2P
2 Credits (15 hours theory and 30 hours practical)
Max Marks:
Theory: 100 (Int: 25; Ext: 75)
Practical: 100
Course Outcomes: Upon completion of the course, students will be able to
CO1: Understand the concepts of webpage, mark up language along with CSS.
CO2: Understand the core concepts of JavaScript including functions, events, DOM manipulation, and form validation.
CO3: Apply AJAX, XML, and JSON to create dynamic and interactive web applications.
Unit I
Introduction to HTML
History of HTML, objectives, basic structures of HTML, header tags, body tags, paragraph tags, and formatting tags.
Tags for form creation: TABLE, FORM, TEXTAREA, SELECT, IMG, IFRAME, FIELDSET, ANCHOR, AUDIO, and VIDEO.
Lists in HTML, introduction to the DIV tag, NAVBAR design.
Introduction to CSS
Types of CSS, selectors, and responsiveness of a web page.
Introduction to Bootstrap
Downloading/linking Bootstrap, using Bootstrap classes, understanding the grid system in Bootstrap.
Bootstrap typography, Jumbotron, button group, Glyphicons, pagination, pager, list group, and carousel.
Introduction to WWW
Protocols and programs, applications and development tools, web browsers, DNS, web hosting providers.
Setting up Windows/Linux/Unix web servers, web hosting in the cloud, and types of web hosting.
Unit II
Introduction to JavaScript
Functions and events, Document Object Model (DOM) traversal using JavaScript.
Output systems in JavaScript: alert, throughput, input box, and console.
Variables and arrays in JavaScript, date, and string handling.
Manipulating CSS through JavaScript
Form validation techniques: required validator, length validator, and pattern validator.
Advanced JavaScript
JavaScript error handling, JavaScript Object-Oriented Programming (OOP), JavaScript libraries and frameworks, JavaScript Browser Object Model (BOM), and ES6 features.
Combining HTML, CSS, and JavaScript
Handling events and buttons, controlling the browser.
Introduction to AJAX
Purpose, advantages, disadvantages, AJAX-based web applications, and alternatives to AJAX.
Introduction to XML
Uses, key concepts, DTD & schemas, XSL, XSLT, XSL elements, and transforming XML using XSLT.
Introduction to XHTML
Key concepts and features.
Introduction to JSON
Keys and values, types of values, arrays, and objects.
Lab Programs
Part – A
- Create your class time table using table tag.
- Design a Webpage for your college containing a description of courses, departments, faculties, library, etc., using list tags, href tags, and anchor tags.
- Create a web page using Frame with rows and columns where you will have a header frame, left frame, right frame, and status bar frame. On clicking in the left frame, information should be displayed in the right frame.
- Create your resume using HTML, using text, link, size, color, and lists.
- Create a Web Page of a supermarket using internal CSS.
- Use inline CSS to format the resume that you have created.
- Use external CSS to format your timetable created.
- Use all the CSS (inline, internal, and external) to format the college web page that you have created.
- Write an HTML program to create your college website for mobile devices.
Part – B
- Write an HTML/JavaScript page to create a login page with validations.
- Develop a simple calculator for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division operations using JavaScript.
- Use regular expressions for validations in the login page using JavaScript.
- Write a program to retrieve data from a text file and display it using AJAX.
- Create an XML file to store Student Information like Register Number, Name, Mobile Number, DOB, and Email-ID.
- Create a DTD for the XML file created.
- Create an XML schema for the XML file created.
- Create an XSL file to convert the XML file to an XHTML file.
- Write a JavaScript program using a switch case.
- Write a JavaScript program using any five events.
- Write a JavaScript program using built-in JavaScript objects.
- Write a program for populating values from JSON text.
- Write a program to transform JSON text into a JavaScript object.

Introduction to HTML
🌐 What is HTML?
HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language. It is the standard markup language used to create and structure web pages.
HTML defines the structure of a webpage using elements (tags). It works together with:
CSS → for styling
JavaScript → for interactivity
🕰 History of HTML
HTML was developed by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989 while working at CERN.
Major Versions:
| Year | Version | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| 1991 | HTML | Basic structure & text formatting |
| 1995 | HTML 2.0 | Forms introduced |
| 1997 | HTML 3.2 | Tables support |
| 1999 | HTML 4.01 | CSS & scripting support |
| 2000 | XHTML | Strict XML-based version |
| 2014 | HTML5 | Multimedia & semantic elements |
HTML5 is the current standard.
🎯 Objectives of HTML
The main objectives of HTML are:
To structure web content
To link web documents (hypertext concept)
To display multimedia content
To create forms for user interaction
To support platform independence
To integrate with CSS and JavaScript
🏗 Basic Structure of HTML
Every HTML document follows a standard structure:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>My Web Page</title>
</head>
<body>
Content goes here
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
<!DOCTYPE html>→ Declares HTML5<html>→ Root element<head>→ Contains metadata<title>→ Page title<body>→ Visible content
🏷 Header Tags
Header tags are used to define headings.
<h3>Section Heading</h3>
There are 6 heading levels: <h1> to <h6>.
📄 Paragraph Tag
Used to define paragraphs.
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
✨ Formatting Tags
Used to format text.
| Tag | Purpose |
|---|---|
<b> | Bold |
<i> | Italic |
<u> | Underline |
<strong> | Important text |
<em> | Emphasized text |
<mark> | Highlight text |
<p><b>Bold</b> and <i>Italic</i> text</p>
📝 Tags for Form Creation
HTML provides various tags for creating forms and user input systems.
<form>
Defines a form.
<form>
Name: <input type=”text”>
</form>
<input>
Used for user input fields (text, password, email, etc.).
<textarea>
Used for multi-line input.
<textarea rows=”4″ cols=”30″></textarea>
<select>
Creates a dropdown list.
<select>
<option>Option 1</option>
<option>Option 2</option>
</select>
<fieldset>
Groups related form elements.
<fieldset>
<legend>Personal Info</legend>
</fieldset>
<table>
Used to create tables.
<table border=”1″>
<tr>
<th>Name</th>
<th>Age</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Aman</td>
<td>21</td>
</tr>
</table>
<img>
Used to display images.
<img src=”image.jpg” alt=”Sample Image”>
<iframe>
Embeds another webpage.
<iframe src=”https://example.com”></iframe>
<a> (Anchor Tag)
Used to create hyperlinks.
<a href=”https://example.com”>Visit Website</a>
<audio>
Embeds audio content.
<audio controls>
<source src=”audio.mp3″>
</audio>
<video>
Embeds video content.
<video width=”320″ controls>
<source src=”video.mp4″>
</video>
📋 Lists in HTML
HTML supports three types of lists:
1️⃣ Ordered List
<ol>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
</ol>
2️⃣ Unordered List
<ul>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
</ul>
3️⃣ Definition List
<dl>
<dt>HTML</dt>
<dd>HyperText Markup Language</dd>
</dl>
📦 Introduction to the Tag
The <div> tag is used to group elements together.
It is commonly used for layout and styling.
<div>
<h2>Section Title</h2>
<p>Content here</p>
</div>
The <div> tag is used to group elements together.
It is commonly used for layout and styling.
<div>
<h2>Section Title</h2>
<p>Content here</p>
</div>
🧭 NAVBAR Design (Basic Example)
A navigation bar (navbar) is used for website navigation.
<nav>
<a href=”#”>Home</a>
<a href=”#”>About</a>
<a href=”#”>Contact</a>
</nav>
Using CSS, it can be styled horizontally.
🎯 Exam Important Points
- HTML stands for HyperText Markup Language.
- Developed by Tim Berners-Lee.
- HTML structure includes html, head, and body tags.
- Forms use form, input, textarea, select tags.
- Lists: ordered, unordered, definition.
- Div is used for grouping content.
- Anchor tag creates hyperlinks.
- HTML5 supports audio and video.

📘 Introduction to CSS
🌐 What is CSS?
CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets.
It is used to control the appearance, layout, and design of web pages. While HTML provides structure, CSS makes the webpage visually attractive.
With CSS, you can control:
Colors
Fonts
Spacing
Layout
Alignment
Responsive behavior
🎯 Why CSS is Important
Separates content from design
Improves website appearance
Makes pages responsive
Reduces code repetition
Enhances user experience
🧩 Types of CSS
There are three types of CSS:
1️⃣ Inline CSS
CSS is written directly inside the HTML element using the style attribute.
Example:
Advantages:
Easy to use
Useful for quick styling
Disadvantages:
Not reusable
Makes code messy
2️⃣ Internal CSS
CSS is written inside the <style> tag within the <head> section.
Example:
<head>
<style>
p {
color: red;
font-size: 18px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<p>This is a paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html>
Advantages:
Applies to the whole page
Better than inline CSS
Disadvantages:
Only works for one HTML page
3️⃣ External CSS
CSS is written in a separate .css file and linked to the HTML document.
Example:
HTML File:
style.css:
font-size: 16px;
}
Advantages:
Reusable
Cleaner code
Best practice in web development
🎯 CSS Selectors
Selectors are used to select HTML elements that you want to style.
1️⃣ Element Selector
Selects elements by tag name.
}
2️⃣ ID Selector
Selects an element with a specific id.
}
HTML:
<h1 id=“heading”>Title</h1>
3️⃣ Class Selector
Selects elements with a specific class.
.box {
background-color: yellow;
}
HTML:
<div class=“box”>Content</div>
4️⃣ Universal Selector
Selects all elements.
padding: 0;
}
5️⃣ Group Selector
Applies the same style to multiple elements.
}
📱 Responsiveness of a Web Page
Selectors are used to select HTML elements that you want to style.
🌍 What is Responsive Design?
Responsive design means that a website automatically adjusts its layout according to different screen sizes such as:
Mobile
Tablet
Laptop
Desktop
🔹 Why Responsiveness is Important
Improves user experience
Mobile-friendly design
Better SEO ranking
Works on all devices
Media Queries in CSS
Media queries are used to apply CSS rules based on screen size.
Example:
background-color: lightblue;
}
}
If the screen width is 600px or less, the background color changes.
Flexible Units
Responsive design uses:
%(percentage)emremvhvw
Instead of fixed units like px.
Responsive Images
height: auto;
}
📊 Summary Table
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| CSS | Used for styling web pages |
| Types of CSS | Inline, Internal, External |
| Selectors | Element, ID, Class, Universal |
| Responsiveness | Adjust layout for different devices |
| Media Queries | Apply styles based on screen size |
🎯 Exam Important Points
- CSS stands for Cascading Style Sheets.
- Three types: Inline, Internal, External.
- External CSS is best practice.
- Selectors are used to target HTML elements.
- Media queries make websites responsive.
- Responsive design improves mobile usability.
📝 Short Revision Notes
- CSS styles HTML pages.
- Three types of CSS.
- Selectors target elements.
- Media queries enable responsive design.
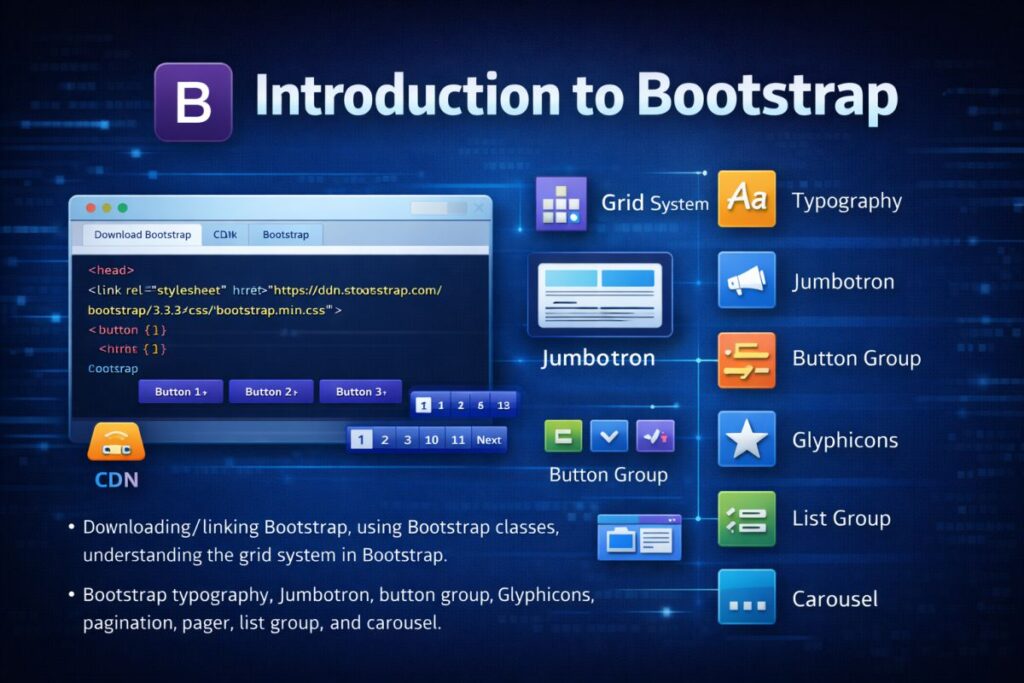
Introduction to Bootstrap
🌐 What is Bootstrap?
Bootstrap is a front-end framework used for designing responsive and mobile-first websites quickly and easily.
It includes:
Predefined CSS classes
JavaScript components
Grid system
Responsive utilities
Bootstrap reduces development time and ensures consistent design.
🎯Why Use Bootstrap?
Mobile-first design
Responsive layout
Pre-designed components
Cross-browser compatibility
Easy to use
Bootstrap was originally developed by Twitter.
📥 Downloading / Linking Bootstrap
There are two main ways to use Bootstrap:
1️⃣ Using CDN (Recommended Method)
You can link Bootstrap directly from a Content Delivery Network (CDN).
<link href=”https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/bootstrap@5.3.2/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css” rel=”stylesheet”>
For JavaScript:
Advantages:
No need to download files
Fast loading
Easy setup
2️⃣ Downloading Bootstrap
Steps:
Go to the official website:
BootstrapDownload the ZIP file.
Extract and link the CSS and JS files manually.
Example:
🎨 Using Bootstrap Classes
Bootstrap provides predefined classes for styling.
Example:
<button class=“btn btn-primary”>Click Me</button>
Common classes:
containerrowcolbtntext-centerbg-primarycard
🧩 Understanding the Grid System
Bootstrap uses a 12-column grid system. It helps create responsive layouts.
Basic Grid Example
<div class=“col-md-6”>Left Side</div>
<div class=“col-md-6”>Right Side</div>
</div>
</div>
container→ Main wrapperrow→ Horizontal rowcol-md-6→ 6 columns (half width on medium screens)
🔹 Breakpoints in Bootstrap
| Class | Screen Size |
|---|---|
| col-sm | Small devices |
| col-md | Medium devices |
| col-lg | Large devices |
| col-xl | Extra large devices |
✍ Bootstrap Typography
Bootstrap provides ready-made typography classes.
Examples:
<p class=“fw-bold”>Bold text</p>
Common classes:
leadtext-primarytext-centerfw-boldtext-muted
🏗 Jumbotron
Jumbotron is used to highlight important content.
(Note: Removed in Bootstrap 5, but still important for exams.)
Example (Bootstrap 4 style):
<p>This is a Jumbotron.</p>
</div>
Purpose:
Display featured content
Highlight important announcements
🔘 Button Group
Used to group multiple buttons together.
<button class=“btn btn-primary”>Middle</button>
<button class=“btn btn-primary”>Right</button>
</div>
🎯 Glyphicons
Glyphicons are icon fonts used in Bootstrap 3.
Example:
Note:
Glyphicons are not included in Bootstrap 4 and 5 by default.
📄 Pagination
Used to create page navigation links.
<ul class=“pagination”>
<li class=“page-item”><a class=“page-link” href=“#”>1</a></li>
<li class=“page-item”><a class=“page-link” href=“#”>2</a></li>
</ul>
📌 Pager
Pager provides simple previous and next navigation.
Example (Bootstrap 3 style):
<li><a href=“#”>Next</a></li>
</ul>
📋 List Group
Used to create styled lists.
<li class=“list-group-item”>Item 2</li>
</ul>
🎞 Carousel
Carousel is used to create image sliders.
<div class=“carousel-item active”>
<img src=“image1.jpg” class=“d-block w-100”>
</div>
<div class=“carousel-item”>
<img src=“image2.jpg” class=“d-block w-100”>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Uses:
Image sliders
Banner sections
Featured content
📊 Summary Table
| Feature | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Grid System | Responsive layout |
| Typography | Styled text |
| Jumbotron | Highlight content |
| Button Group | Group buttons |
| Glyphicons | Icons |
| Pagination | Page navigation |
| List Group | Styled lists |
| Carousel | Image slider |
🎯 Exam Important Points
- Bootstrap is a front-end framework.
- It uses a 12-column grid system.
- CDN is the easiest way to use Bootstrap.
- Grid system ensures responsive design.
- Jumbotron highlights important content.
- Carousel creates image sliders.
- Pagination is used for page navigation.
📝 Short Revision Notes
- Bootstrap simplifies web design.
- Mobile-first framework.
- 12-column responsive grid.
- Predefined classes save time.
- Includes UI components like carousel and list groups.
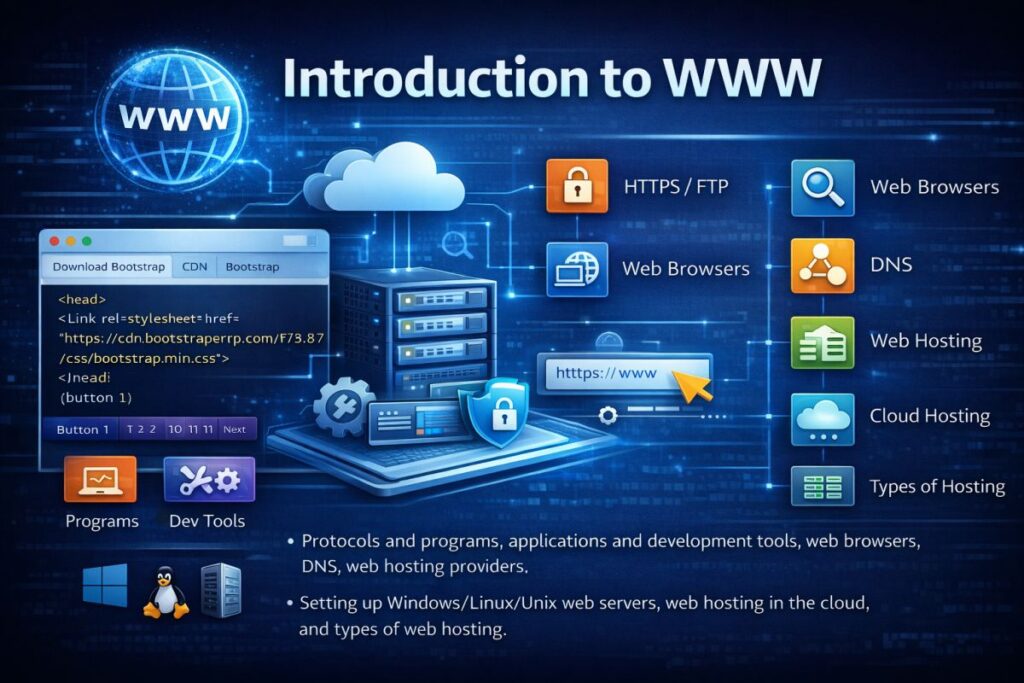
Introduction to WWW (World Wide Web)
🌐 What is WWW?
The World Wide Web (WWW) is a system of interconnected web pages and resources that are accessed through the Internet using web browsers.
It was invented by Tim Berners-Lee in 1989.
WWW works on three main technologies:
- HTML (structure)
- URL (address)
- HTTP (communication protocol)
🌍 Components of WWW
- Web Browser
- Web Server
- Protocols
- DNS
Hosting
🔗 Protocols and Programs
🌐 What is a Protocol?
A protocol is a set of rules that allows communication between devices over the Internet.
🔹 Important Internet Protocols
1️⃣ HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol)
- Used to transfer web pages.
- Works between browser and server.
- Default port: 80
2️⃣ HTTPS (Secure HTTP)
- Secure version of HTTP.
- Uses encryption (SSL/TLS).
- Default port: 443
3️⃣ FTP (File Transfer Protocol)
Used to transfer files between computers.
4️⃣ SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol)
Used to send emails.
💻 Programs Used in WWW
- Web Browsers
- Web Servers
- FTP Clients
- Email Clients
🛠 Applications and Development Tools
Web development requires various tools.
🔹 Front-End Tools
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
🔹 Back-End Tools
- PHP
- Python
- Node.js
- Java
🔹 Development Tools
- Code Editors (VS Code, Notepad++)
- Browsers (for testing)
- Local servers (XAMPP, WAMP)
🌐 Web Browsers
A web browser is software used to access websites.
Popular web browsers:
- Google Chrome
- Mozilla Firefox
- Microsoft Edge
- Safari
Functions of a Web Browser:
- Sends request to server
- Receives response
- Displays web page
🌎 DNS (Domain Name System)
DNS converts domain names into IP addresses.
Example:
- Domain:
www.google.com - IP Address: 142.250.182.14
DNS acts like a phonebook of the Internet.
Without DNS, we would need to remember IP addresses instead of names.
🏢 Web Hosting Providers
Web hosting providers store website files on servers so they can be accessed online.
Popular hosting providers:
- GoDaddy
- Hostinger
- Bluehost
- Amazon Web Services
🖥 Setting Up Web Servers
A web server stores and delivers web pages to users.
🔹 Web Server on Windows
- Install XAMPP or WAMP
- Start Apache server
- Place website files inside
htdocsfolder - Access via:
http://localhost
🔹 Web Server on Linux
Install Apache using terminal:
sudo apt install apache2Access via browser using server IP address.
🔹 Web Server on Unix
- Install Apache or Nginx
- Configure server settings
- Start service
Common Web Server Software:
- Apache
- Nginx
- IIS
☁ Web Hosting in the Cloud
Cloud hosting stores websites on multiple servers.
Example:
- Amazon Web Services
- Google Cloud
- Microsoft Azure
Advantages:
- High availability
- Scalability
- Better performance
- Pay-as-you-use model
🏷 Types of Web Hosting
🔹 1️⃣ Shared Hosting
- Multiple websites share one server.
- Low cost.
- Suitable for small websites.
🔹 2️⃣ VPS Hosting (Virtual Private Server)
- Virtual server environment.
- More control than shared hosting.
🔹 3️⃣ Dedicated Hosting
- Entire server dedicated to one website.
- High performance.
- Expensive.
🔹 4️⃣ Cloud Hosting
- Hosted on multiple connected servers.
- High scalability and reliability.
📊 Summary Table
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| WWW | System of interconnected web pages |
| HTTP | Transfers web pages |
| DNS | Converts domain to IP |
| Web Browser | Displays websites |
| Web Server | Stores website files |
| Shared Hosting | Multiple sites, low cost |
| Cloud Hosting | Scalable & reliable |
🎯 Exam Important Points
- WWW invented by Tim Berners-Lee.
- HTTP and HTTPS are communication protocols.
- DNS converts domain names to IP addresses.
- Web browsers display web pages.
- Apache and Nginx are web servers.
- Cloud hosting provides scalability.
- Types of hosting: Shared, VPS, Dedicated, Cloud.
📝 Short Revision Notes
- WWW = Web system accessed via Internet.
- Uses HTTP, DNS, and Web Browsers.
- Hosting stores website files.
- Cloud hosting is scalable and reliable.